在开发 WinForms 应用程序时,有时需要防止同一个应用程序的多个实例同时运行。这种需求在某些情况下非常重要,例如,当你需要确保某个资源(如文件或数据库)只被一个应用实例访问时。
本文将介绍几种防止同一应用运行多个实例的方法,提供详细的代码示例,并输出为 Markdown 格式。
方法一:使用 Mutex 类
Mutex(互斥量)是一个同步基元,它可以用于跨线程和进程同步。通过创建一个命名互斥量,可以防止应用运行多个实例。
示例代码
namespace SingleInstanceApp{ internal static class Program { private static Mutex mutex = null; /// <summary> /// The main entry point for the application. /// </summary> [STAThread] static void Main() { const string mutexName = "MyApp"; bool isOwned;
mutex = new Mutex(true, mutexName, out isOwned);
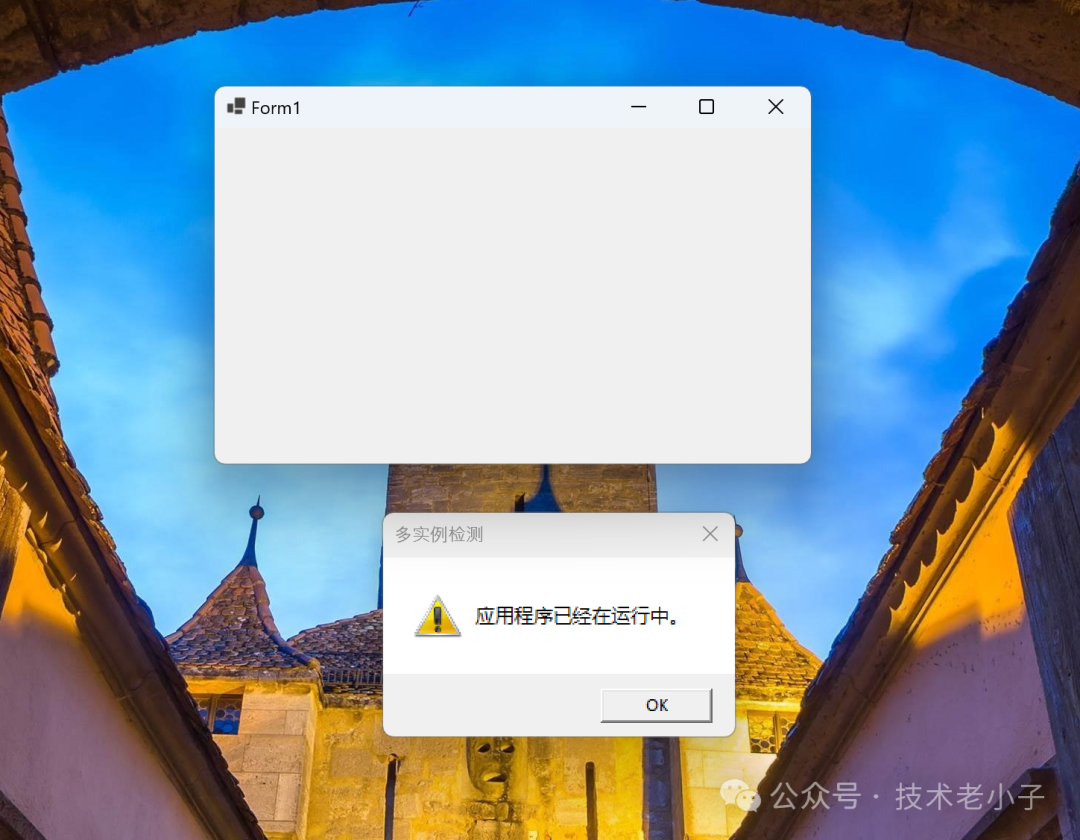
if (!isOwned) { MessageBox.Show("应用程序已经在运行中。", "多实例检测", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Exclamation); return; } // To customize application configuration such as set high DPI settings or default font, // see https://aka.ms/applicationconfiguration. ApplicationConfiguration.Initialize(); Application.Run(new Form1());
GC.KeepAlive(mutex); } }}
在上述代码中,我们使用 Mutex 类创建了一个系统全局命名的互斥体 mutexName。如果应用程序已经在运行,则 isOwned 将为 false,应用会显示一条消息并退出。
方法二:使用 Process 类
通过 Process 类检查当前是否已经有同名进程在运行,也可以防止多个实例的运行。
示例代码
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace SingleInstanceApp{ internal static class Program { /// <summary> /// The main entry point for the application. /// </summary> [STAThread] static void Main() { if (IsAlreadyRunning()) { MessageBox.Show("应用程序已经在运行中。", "多实例检测", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Exclamation); return; } // To customize application configuration such as set high DPI settings or default font, // see https://aka.ms/applicationconfiguration. ApplicationConfiguration.Initialize(); Application.Run(new Form1()); }
static bool IsAlreadyRunning() { string currentProcessName = Process.GetCurrentProcess().ProcessName; Process[] processes = Process.GetProcessesByName(currentProcessName); return processes.Length > 1; } }}
此方法通过 Process.GetProcessesByName 方法获取当前运行的同名进程。如果长度大于1,说明此时已有另一个实例在运行。
方法三:使用 Windows API
还有一种方法是利用 Windows API 创建一个命名事件,检查该事件是否已经存在。
示例代码
using System.Diagnostics;using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace SingleInstanceApp{ internal static class Program { const string UniqueEventName = "Global\\MyApp";
[DllImport("kernel32", SetLastError = true)] static extern IntPtr CreateEvent(IntPtr lpEventAttributes, bool bManualReset, bool bInitialState, string lpName);
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")] static extern uint GetLastError(); /// <summary> /// The main entry point for the application. /// </summary> [STAThread] static void Main() { IntPtr handle = CreateEvent(IntPtr.Zero, false, false, UniqueEventName); if (handle == IntPtr.Zero || GetLastError() == 183) // ERROR_ALREADY_EXISTS (183) { MessageBox.Show("应用程序已经在运行中。", "多实例检测", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Exclamation); return; }
// To customize application configuration such as set high DPI settings or default font, // see https://aka.ms/applicationconfiguration. ApplicationConfiguration.Initialize(); Application.Run(new Form1()); } }}
上述代码使用了 CreateEvent API 创建一个命名事件,并通过 GetLastError 检查事件是否已经存在(错误代码 183 表示该事件已存在)。
CreateEvent 是一个 Windows API 函数,用于创建或打开一个命名的或未命名的事件对象。事件对象在进程间和线程间同步中非常有用。
GetLastError() 函数是用于检索扩展的错误信息的函数。它通常与其他 Windows API 函数一起使用,这些函数不返回明确的错误代码,但是如果调用失败,可以通过 GetLastError() 获取详细的错误信息。
总结
以上介绍了三种在 WinForms 开发中防止同一应用运行多个实例的方法:
使用 Mutex 类。
使用 Process 类。
使用 Windows API。
每种方法都有其优点和适用场景,开发者可根据具体需求选择合适的方法来实现多实例检测功能。希望此文对你有所帮助,欢迎提出任何问题或建议。
该文章在 2024/7/23 22:28:12 编辑过